| In modern Hebrew, the letter Aleph can appear in three forms. Notice that the manual print form of Aleph resembles the book print version—except that the strokes of the lines are all even. You will learn manual print in order to recognize the printed Hebrew letters as they appear in Hebrew texts. You write the manual print version of the letter Aleph according to the following pattern: |
|  |  | | The numbered arrows show the order and direction for drawing the lines (the gray rectangle indicates the letter proportions in a graph paper cell). |
|
 |  | | Manual print is important to learn to help you recognize printed Hebrew type; however, handwritten communication is normally written using Hebrew cursive. You write the cursive version of the letter Aleph according to the following pattern: |
|  |  | | Write the letter from right to left, beginning with the stroke labeled 1 and then to the stroke labeled 2. |
|
 | 
The letter Aleph is the "father" of the Aleph-Bet, whose original pictograph represents an ox, strength, and leader. It's numerical value is one (and also 1,000) and it is a silent letter. Aleph therefore is preeminent in its order and alludes to the ineffable mysteries of the oneness of God. Indeed, the word aluph (derived from the very name of this letter) means "Master" or "Lord."
In the classical Hebrew script (ketav Ashurit) used for writing Torah scrolls, Aleph is constructed with two Yods (one to the upper right and the other to the lower left) that are joined by a diagonal Vav. Ketav Ashurit was the script that Jesus would have read (ketav Ivri was an older script, similar to ancient Phoenician, but was not the script used when Moses received the Torah from the LORD on Sinai. Ketav Ivri is also sometimes called the Temple Script because samples of it are extant dated to the time of Solomon's Temple).
From the Phoenician/Ketav Ivri, the letter Aleph morphed into the Greek letter Alpha 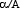 , from which came the Latin A: , from which came the Latin A: |
 | | |  |
 |  | | - Mysteries of Aleph
In Kabbalistic literature, the upper Yod (meaning an arm) represents the hidden (and infinite) aspect of YHVH called ein sof (אֵין סוֹף, lit. "without end"), whereas the lower Yod represents the revelation of YHVH to mankind. The Vav, whose meaning is "hook," shows connectedness between the two realms. Vav is also thought to represent humanity, since Adam was created on the sixth day. Vav is diagonal since it is humbled in the face of God's mystery and His revelation. The two Yods also indicate the paradox of experiencing God as both hidden and close, far and near.
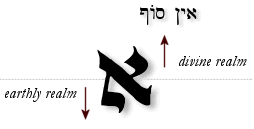
- The Gematria of the Parts of Aleph
The basic gematria for Aleph is one, indicating the One and only God who is the Master of the universe. Note, however, that the gematria for the parts of the letter Aleph add up to 26 (Yod+Yod+Vav). This is the same number as the sacred Name YHVH, also indicating a link between the Aleph and God Himself. This is also demonstrated in Exodus 3:14-15, where the LORD reveals His Name to Moses as ehyeh asher ehyeh (אֶהְיֶה אֲשֶׁר אֶהְיֶה), "I AM THAT I AM."
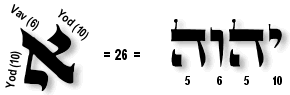
There is a midrash (fable) that asks why Aleph was not selected to be the first letter of the Torah. In the story, all of the letters come before the LORD giving reasons why they should be the first letter - all, that is, except for the letter Aleph. When the LORD asked why, Aleph explained that since he was silent, he had nothing to say. But the LORD honored Aleph's humility and declared him to be the first of all the letters -- and to be honored as the letter of the first word of the Ten Commandments:
אָנכִי יְהוָה אֱלהֶיךָ
- In the Beginning -- Aleph-Tav
In Or Torah, Rabbi Dov Ber, the Maggid of Mezritch, explained first words of Torah: Bereshit Bara Elohim Et - "In the beginning God created et" (Gen 1:1). Note that et is an untranslatable word used to indicate that "a definite direct object is next" (thus there needs to be an et before the heavens and theearth). But Dov Ber points out that et is spelled - Aleph-Tav, an abbreviation for the Aleph-Bet. Aleph is the first letter of the Hebrew alphabet and Tav the last, so, he reasoned, in the beginning God created the Aleph-Bet. Since God did this before creating the heavens and the earth, the letters are considered to be the primordial "building blocks" of all of creation.
Rabbi Shneur Zalman of Liadi stated that if the letters were to depart even for an instant, all of creation would become absolute nothingness (Zalman, Shneur. 1981. "Igeret Hateshuvah." Likkutie Amarim - Tanya. Brooklyn: Kihot. 289).
- Aleph and the Divine Names
There are a number of divine Names that begin with the letter Aleph, including the following:
|
|
|
No comments:
Post a Comment